classify takes the present image (img)
classify2 ...
showClasses : modifie la valeur de chaque pixel,
créant une teinte uniforme pour chaque classe, et l’affiche
classe_to_region (or ctr) makes a segmentation from the existing classes
declass suppresses the existing classification
General considerations about classes, see diccan item.
A class is a subset of an image, containing all the points sharing a common feature. You can for instance consider the set of colors as a set of classes. But, generally, it is of little interest, and we look for more restrictive classifications. Some of the operations we have shown about colors create by themselves clasifications (notably all the palettes).
You can also look for "meaningful", "semantic" classifications. For instance classify has been built to recognize subject types : country, city, interior, head, academy.
Note that !
- the pixels contained in a class can be placed anywhere in the image, whithout being joined.
- a pixel can belong to several classes
When Roxame classifies the pixels, it does it with the creation of integers array of the same size as the image, and noting for each point the classes where it belongs.
The code ; A_Measure
1. class computation for each pixel
In a first pass, all the posisioins of class[][] are set at 0
1. blues add 1
2. lights: add 2
4. vivid add 4
8 greens add 8
16 carnations add 16
neutrals add 32
grays add 64
if none of theses classes has been found, we are in the gray clases, from 1000 to 1003
then tabclass array, from 0 to 6
int[][] classe. the classe of each pixel in the migage
int[][]tablass value of each class (??)
int ecl
int[]classecard, number of pixels in the class
int[][][][]tabval
floar midiangrid, medianuf
boolean mediantag$int lobpic, hobpix
int[][] semclass (on the total width of the image)
The basic array is classe[x][y].
nbregText : displays the number of regions
Segment0 : segmentation on the displayed image. Note : to get valuavble results, this segmentation must not be applied to a complex iemage (notably a photographic picture). Use it for simple images, got direcdtly of after filters applications. Our other segmentations are in fact the combination of simplifications with a final call to SegmentO.
Segment1 : begins by a classification an aligns the pixels on their classes, then applies Segment0
Segment2 : sorts the colors on 8 classes and applies Segment 0.
Segment3 :simplifies by pixelization (1/2), VGA paletete ane median. More brutal and less subtle than Segment2.
Segment6 : segmentation après une classification conçue spécialement pour le portrait
reseg divides the number or regions by 10
deseg suppresses the segmentation
morphsegreg is a kind of filter, or image generator, but with poor results
Régions particulières :
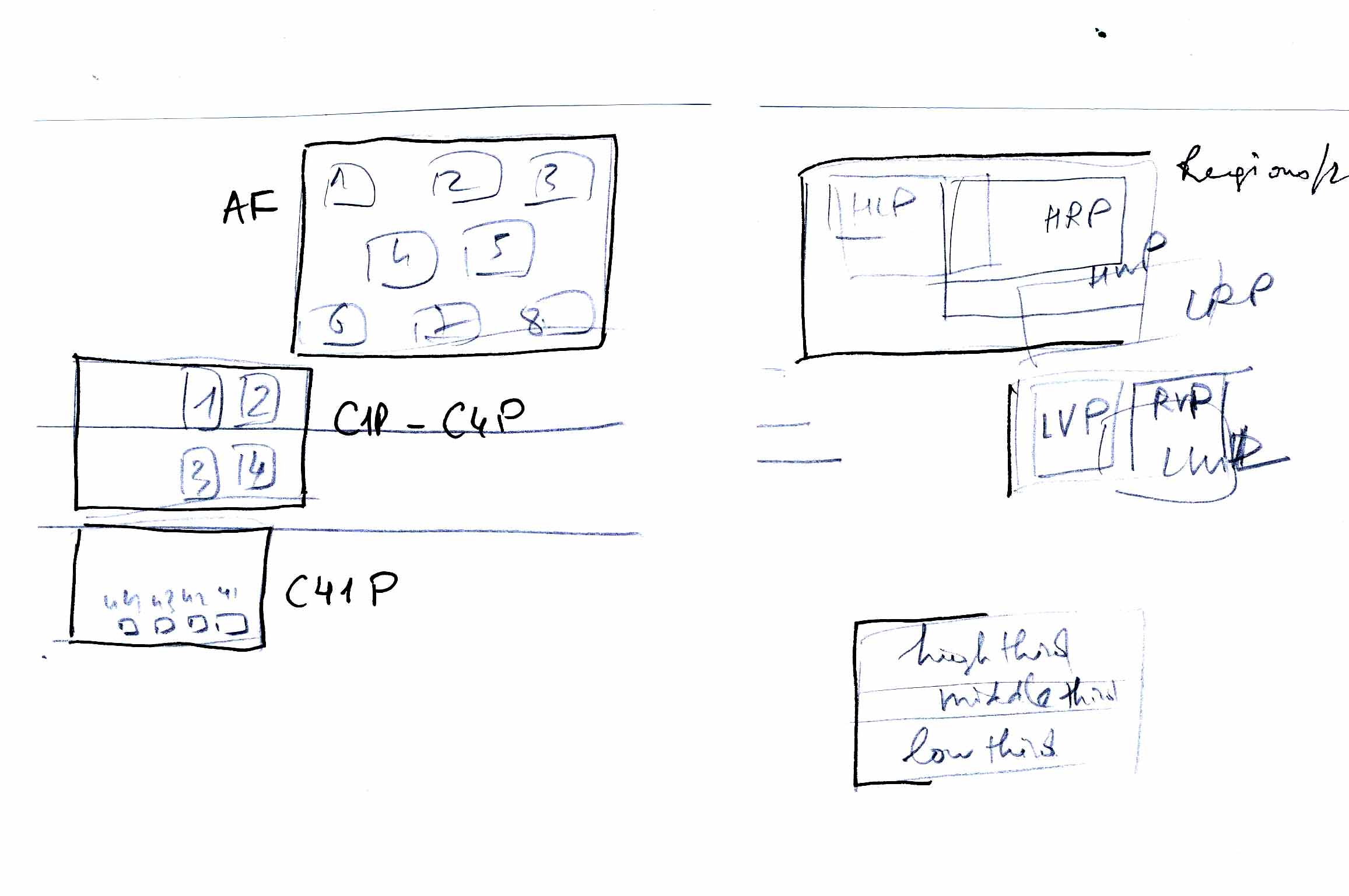
AF1 ,
AF2
AF3
AF4
AF5
AF6
AF7
AF8
C1P
C2P
C3P
C41P
C42P
C43P
C44P
C4P
HLP
HRP
HWP
LRP
LVP
LWL
LWP
R0
RVP
alphonse
centerP
high_third
low_third
middle_third
random_reg
tessel4_1
tessel4_2
tessel4_3
tessel4_4
tessel9_1
tessel9_2
tessel9_3
tessel9_4
tessel9_5
tessel9_6
tessel9_7
tessel9_8
tessel9_9
General considerations about regions and segmentation. See diccan's segmentation item.
A region is a connected subset of pixels.
Segmentation is the partition of the image into a set of regions. We do that with the creation of an array of integers giving for each pixels the number of the region it belongs to.
Beware : segmentaion may take a lot of time (more than one minute on a 640x480 pixels).
The major use of regions is that they afford to apply operations separately to each region, notably filters, grdations and geometric forms generation.
A simplfied image of the regions, with arbitrary colors, is displayed in the low part of the Roxame's scree
Regions are numbered from 1. At start, of after a desegmentation, there is only the 2 oregion. The selection of region is done by the function R, which notably computes the coordinates of the rectangle circumscribing the region. A call to region 0 points on the whole of the region.
At the the limit, we could have as many regions as pixels. Good segmentations, in our experience, have typically some thousands of regions.
The code ; Roxame
int[][]region
int regone, nnbreg
int nbregutil : number of regions operational at a given time
boolean[] regocc
int cardreg,
int xd,yd, xf, yf : coordinates of the rectangles circumscribing the region
